Understanding Tone Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide

Have you ever wondered how those stunning HDR images and videos are displayed on your standard LDR screen? The magic behind this lies in a process called Tone Mapping. Let’s dive deep into the world of Tone Mapping and explore its various aspects.
What is Tone Mapping?
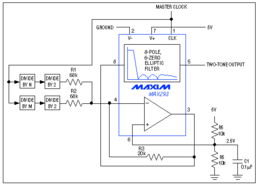
Tone Mapping is a technique used to convert High Dynamic Range (HDR) images or videos into a format that can be displayed on Low Dynamic Range (LDR) devices like standard monitors and TVs. It essentially compresses the wide range of brightness and color values captured by HDR content into a smaller range that can be displayed on LDR screens.
Why is Tone Mapping Necessary?
Human eyes can perceive a dynamic range of approximately 10^5 to 10^6, while cameras and other imaging devices can capture a much wider range, often up to 10^9 or more. However, standard LDR screens can only display a limited range of brightness and color values, typically around 10^8. Tone Mapping helps bridge this gap by compressing the HDR content into a format that can be accurately represented on LDR screens.
How Does Tone Mapping Work?
Tone Mapping works by adjusting the brightness and contrast of the HDR content to fit the LDR display’s capabilities. This process involves several steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Input HDR Content | The process begins with HDR content, which contains a wide range of brightness and color values. |
| Mapping Brightness Levels | The brightness levels of the HDR content are mapped to the LDR display’s brightness range. |
| Adjusting Contrast | The contrast of the mapped content is adjusted to ensure that details in both bright and dark areas are visible. |
| Output LDR Content | The final step involves outputting the adjusted content in a format suitable for LDR displays. |
Types of Tone Mapping Algorithms
There are several Tone Mapping algorithms available, each with its own approach to compressing HDR content. Some of the most popular algorithms include:
- Reinhard Tone Mapping: This algorithm is known for its simplicity and effectiveness in preserving details in both bright and dark areas.
- Drago Tone Mapping: This algorithm is designed to enhance the contrast and details in HDR images while minimizing the loss of information.
- Logarithmic Tone Mapping: This algorithm uses a logarithmic scale to compress the brightness range, resulting in a more natural-looking image.
Adaptive Tone Mapping
Adaptive Tone Mapping is a more advanced technique that adjusts the Tone Mapping process dynamically based on the content of the image or video. This approach allows for better preservation of details and a more natural-looking output. Adaptive Tone Mapping algorithms analyze the content and adjust the Tone Mapping parameters accordingly.
Benefits of Tone Mapping
Tone Mapping offers several benefits, including:
- Improved Visual Quality: Tone Mapping helps preserve details and contrast in both bright and dark areas, resulting in a more visually appealing image or video.
- Compatibility with LDR Devices: Tone Mapping allows HDR content to be displayed on standard LDR screens, making it accessible to a wider audience.
- Enhanced Creativity: Tone Mapping provides artists and creators with more control over the final appearance of their work, allowing them to achieve specific visual effects.
Conclusion
Tone Mapping is a crucial technique that enables the display of HDR content on LDR devices. By compressing the wide range of brightness and color values captured by HDR content, Tone Mapping ensures that viewers can enjoy the full visual experience on their standard screens. As technology continues to evolve, Tone Mapping algorithms will likely become even more sophisticated, providing even better results in the future.



